When users search for "laser chiller", they are usually looking for a clear answer to three practical questions: What is a laser chiller? Why does a laser need it? And how do I choose the right one for my application?
This article provides a practical, easy-to-understand overview of laser chillers, their role in laser systems, and how different types of laser chillers are used across industrial and precision applications.
What Is a Laser Chiller?
A laser chiller is a closed-loop water cooling system designed to control the operating temperature of laser equipment. During laser operation, a significant amount of heat is generated by the laser source and optical components. Without stable cooling, excessive heat can lead to power instability, reduced processing accuracy, and premature component failure.
Unlike simple fans or open water tanks, a professional laser chiller continuously circulates temperature-controlled coolant, removes heat through refrigeration, and maintains a stable water temperature within a narrow range. This makes laser chillers essential for modern laser cutting, welding, marking, cleaning, and precision laser processing systems.
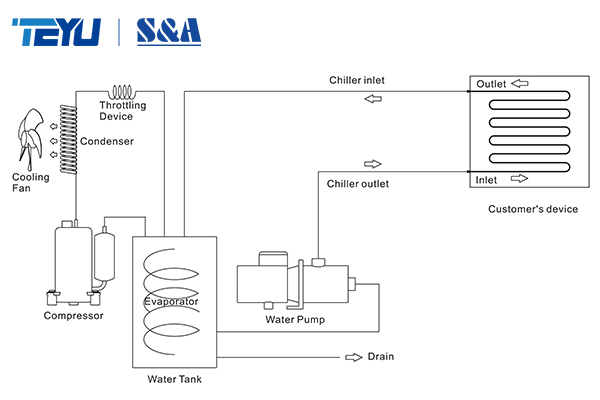
Why Do Laser Machines Need a Chiller?
One of the most common user questions is: "Can a laser run without a chiller?" In practice, most industrial and precision laser systems require a dedicated laser chiller for reliable operation.
Key reasons include:
* Thermal stability: Even small temperature fluctuations can affect laser wavelength, beam quality, and output power.
* Equipment protection: Overheating may damage laser sources, optics, or power modules.
* Consistent processing quality: Stable cooling helps ensure uniform cutting edges, welding seams, or marking results.
* Longer service life: Controlled operating temperatures reduce thermal stress on components.
As laser power levels increase and applications become more precise, the importance of a stable laser chiller becomes even more critical.
How to Choose the Right Laser Chiller
When selecting a laser chiller, users typically compare more than just cooling capacity. Important factors include:
* Laser type and power level (CO2, fiber, UV, ultrafast)
* Required temperature stability
* Cooling capacity and heat load
* Installation space and form factor
* Alarm and protection functions
* Communication and control options
A well-matched laser chiller not only protects the laser system but also improves production efficiency and reduces downtime.
Beyond Lasers: Where Laser Chiller Technology Is Also Used
Although designed for lasers, the same cooling principles are applied in other heat-sensitive equipment, such as:
* CNC spindles and machine tools
* UV curing and printing systems
* 3D printing and additive manufacturing
* Optical instruments and laboratory equipment
This versatility explains why laser chiller technology has become a standard solution across multiple industries.
Conclusion: Understanding "Laser Chiller" Before Making a Choice
For users searching for a "laser chiller", the goal is not just to find a chiller product, but to understand how proper cooling directly affects laser performance, reliability, and processing quality. By identifying the laser type, power level, and precision requirements, users can narrow down the most suitable cooling solution, whether for CO2 lasers, fiber lasers, handheld systems, or high-precision applications.
A clear understanding of laser chiller fundamentals makes it easier to evaluate different product series and select a solution that truly fits the application.






