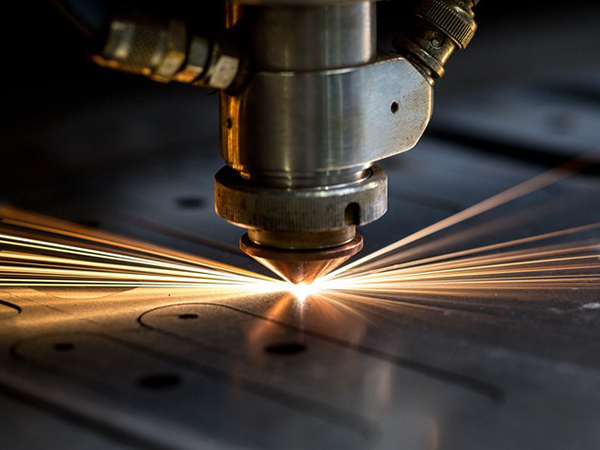
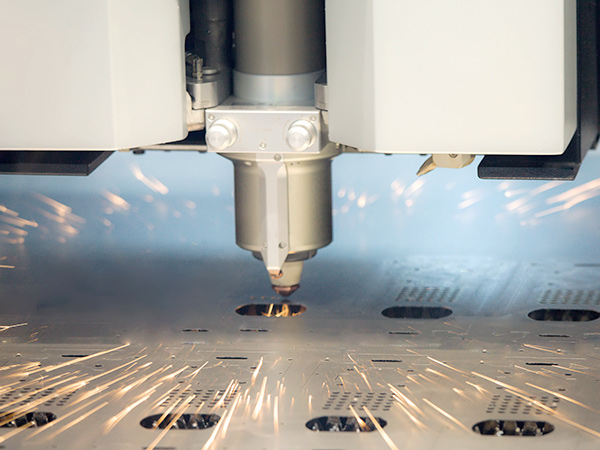
In the past three years, due to the pandemic, the growth rate of industrial laser demand has slowed. However, the development of laser technology has not stopped. In the field of fiber lasers, ultra-high power fiber lasers of 60kW and above have been successively launched, pushing the power of industrial lasers to another level.
How much demand is there for high power lasers above 30,000 watts?
For multi-mode continuous fiber lasers, increasing the power by adding modules seems to be the agreed-upon way. In the past few years, the power has increased by 10,000 watts each year. However, the realization of industrial cutting and welding for ultra-high power lasers is even more difficult and requires higher stability. In 2022, the power of 30,000 watts will be used on a large scale in laser cutting, and 40,000 watts of equipment is currently in the exploration stage for small-scale application.
In the era of kilowatt fiber lasers, powers below 6kW can be used for cutting and welding of most common metal products, such as elevators, cars, bathrooms, kitchenware, furniture, and chassis, with thicknesses not exceeding 10mm for both sheet and tube materials. The cutting speed of a 10,000-watt laser is twice that of a 6,000-watt laser, and the cutting speed of a 20,000-watt laser is more than 60% higher than that of a 10,000-watt laser. It also breaks the thickness limit and can cut carbon steel over 50mm, which is rare in general industrial products. So how about high power lasers above 30,000 watts?
Application of high-power lasers to improve shipbuilding quality
In April of this year, French President Macron visited China, accompanied by companies such as Airbus, DaFei Shipping, and French power supplier Électricité de France.
Airbus, the French aircraft manufacturer, announced a bulk purchase agreement with China for 160 aircraft, with a total value of approximately $20 billion. They will also be constructing a second production line in Tianjin. China Shipbuilding Group Corporation signed a cooperation agreement with French company DaFei Shipping Group, including the construction of 16 super large container ships of Type 2, with a value of over 21 billion yuan. China General Nuclear Power Group and Électricité de France have close cooperation, with the Taishan Nuclear Power Plant being a classic example.

High-power laser equipment ranging from 30,000 to 50,000 watts has the cutting capability for steel plates over 100mm thick. Shipbuilding is an industry that extensively uses thick metal plates, with typical commercial ships having hull steel plates with a thickness of over 25mm, and large cargo ships even surpassing 60mm. Large warships and super large container ships may use specialty steels with a thickness of 100mm. Laser welding has faster speeds, less heat deformation and rework, higher weld quality, reduced filler material consumption, and significantly improved product quality. With the emergence of lasers with tens of thousands of watts of power, there are no longer limitations in laser cutting and welding for shipbuilding, opening up great potential for future substitution.
Luxury cruise ships have been considered the pinnacle of the shipbuilding industry, traditionally monopolized by a few shipyards such as Italy's Fincantieri and Germany's Meyer Werft. Laser technology has been extensively used for material processing in the early stages of ship construction. China's first domestically produced cruise ship is planned to be launched by the end of 2023. China Merchants Group has also advanced the construction of a laser processing center in Nantong Haitong for their cruise ship manufacturing project, which includes a high-power laser cutting and welding thin plate production line. This application trend is expected to gradually penetrate civilian commercial ships. China has the most shipbuilding orders in the world, and the role of lasers in the cutting and welding of thick metal plates will continue to grow.

Application of 10kW+ lasers in aerospace
Aerospace transportation systems primarily include rockets and commercial aircraft, with weight reduction being a key consideration. This imposes new requirements for cutting and welding aluminum and titanium alloys. Laser technology is essential for achieving high-precision welding and cutting assembly processes. The emergence of 10kW+ high-power lasers has brought comprehensive upgrades to the aerospace field in terms of cutting quality, cutting efficiency, and high-integration intelligence.
In the manufacturing process of the aerospace industry, there are many components that require cutting and welding, including engine combustion chambers, engine casings, aircraft frames, tail wing panels, honeycomb structures, and helicopter main rotors. These components have extremely strict requirements for cutting and welding interfaces.
Airbus has been using high-power laser technology for a long time. In the manufacturing of the A340 aircraft, all aluminum alloy internal bulkheads are welded using lasers. Breakthrough progress has been made in the laser welding of fuselage skins and stringers, which has been implemented on the Airbus A380. China has successfully test-flown the domestically-produced C919 large aircraft and will deliver it this year. There are also future projects such as the development of the C929. It can be foreseen that lasers will have a place in the manufacturing of commercial aircraft in the future.

Laser technology can aid in the safe construction of nuclear power facilities
Nuclear power is a new form of clean energy, and the United States and France have the most advanced technology in the construction of nuclear power plants. Nuclear power accounts for approximately 70% of France's electricity supply, and China cooperated with France in the early stages of its nuclear power facilities. Safety is the most important aspect of nuclear power facilities, and there are many metal components with protective functions that require cutting or welding.
China's independently developed laser intelligent tracking MAG welding technology has been mass-applied in the steel liner dome and barrel of Units 7 and 8 at the Tianwan Nuclear Power Plant. The first nuclear-grade penetration sleeve welding robot is currently being prepared.
Following the trend of laser development, Teyu launched the CWFL-60000 ultrahigh power fiber laser chiller.
Teyu has kept up with the trend of laser development and has developed and produced the CWFL-60000 ultrahigh power fiber laser chiller, which provides stable cooling for 60kW laser equipment. With a dual independent temperature control system, it is able to cool both the high-temperature laser head and a low-temperature laser source, providing a stable output for laser equipment and effectively guaranteeing the fast and efficient operation of high-power laser cutting machines.

The breakthrough in laser technology has given birth to a wide market for laser processing equipment. Only with the right tools can one stay ahead in the fierce market competition. With the need for transformation and upgrading in high-end applications such as aerospace, shipbuilding, and nuclear power, the demand for thick plate steel processing is increasing, and high-power lasers will assist in the accelerated development of the industry. In the future, ultra-high power lasers with a power of over 30,000 watts will be mainly used in heavy industry fields such as wind power, hydropower, nuclear power, shipbuilding, mining machinery, aerospace, and aviation.
Source: https://www.teyuchiller.com/application-of-high-power-lasers-in-high-tech-and-heavy-industries