Laser manufacturing technology has seen rapid development over the past decade, with its primary application being laser processing for metal materials. Laser cutting, laser welding, and laser cladding of metals are among the most important processes in metal laser processing. However, as concentration increases, the homogenization of laser products has become severe, limiting the growth of the laser market. Therefore, to break through, laser applications must expand into new material domains. Non-metallic materials suitable for laser application include fabrics, glass, plastics, polymers, ceramics, and more. Each material involves multiple industries, but mature processing techniques already exist, making laser substitution not an easy task.
To enter a non-metallic material field, it is necessary to analyze whether laser interaction with the material is feasible and whether adverse reactions will occur. Currently, glass stands out as a major area with high added value and potential for batch laser processing applications.
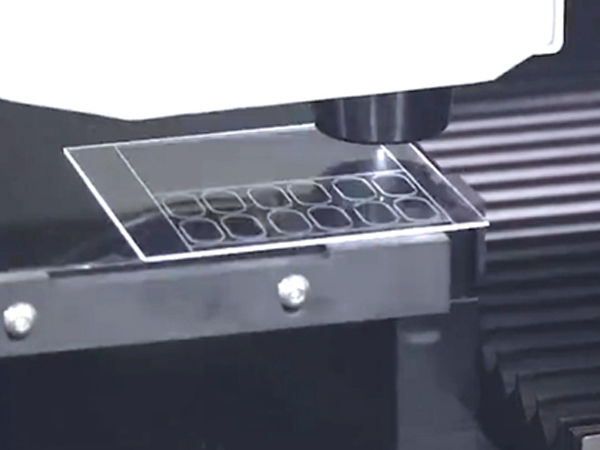

Large Space for Glass Laser Cutting
Glass is an important industrial material used in various industries such as automotive, construction, medical, and electronics. Its applications range from small-scale optical filters measuring micrometers to large-scale glass panels used in industries like automotive or construction.
Glass can be categorized into optical glass, quartz glass, microcrystalline glass, sapphire glass, and more. Glass's significant characteristic is its brittleness, which poses significant challenges for traditional processing methods. Traditional glass cutting methods typically use hard alloy or diamond tools, with the cutting process divided into two steps. Firstly, a crack is created on the glass surface using a diamond-tipped tool or a hard alloy grinding wheel. Secondly, mechanical means are employed to separate the glass along the crack line. However, these traditional processes have clear drawbacks. They are relatively inefficient, resulting in uneven edges that often require secondary polishing, and they produce a lot of debris and dust. Moreover, for tasks such as drilling holes in the middle of glass panels or cutting irregular shapes, traditional methods are quite challenging. This is where the advantages of laser cutting glass become apparent. In 2022, China's glass industry sales revenue was approximately 744.3 billion yuan. The penetration rate of laser cutting technology in the glass industry is still in its initial stage, indicating a significant space for the application of laser cutting technology as a substitute.
Glass Laser Cutting: From Mobile Phones Onward
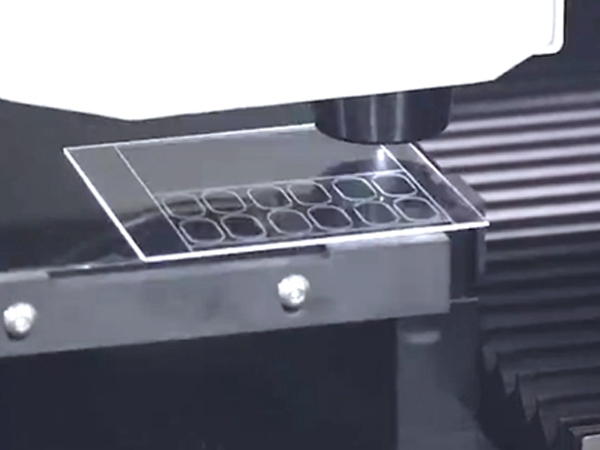
Glass laser cutting often employs a Bezier focusing head to generate high peak power and density laser beams within the glass. By focusing the Bezier beam inside the glass, it instantaneously vaporizes the material, creating a vaporization zone, which rapidly expands to form cracks on the upper and lower surfaces. These cracks form the cutting section composed of countless tiny pore points, achieving cutting through external stress fractures.
With significant advancements in laser technology, power levels have also increased. A nanosecond green laser with over 20W power can effectively cut glass, while a picosecond ultraviolet laser with over 15W power effortlessly cuts glass under 2mm thick. There exist Chinese enterprises that can cut glass up to 17mm thick. Laser cutting glass boasts high efficiency. For instance, cutting a 10cm diameter glass piece on a 3mm thick glass takes only around 10 seconds with laser cutting compared to several minutes with mechanical knives. Laser-cut edges are smooth, with a notch accuracy of up to 30μm, eliminating the need for secondary machining for general industrial products.
Laser-cutting glass is a relatively recent development, starting around six to seven years ago. The mobile phone manufacturing industry was among the early adopters, using laser cutting on camera glass covers and experiencing a surge with the introduction of a laser invisibility cutting device. With the popularity of full-screen smartphones, precise laser cutting of entire large-screen glass panels has significantly boosted glass processing capacity. Laser cutting has become common when it comes to glass component processing for mobile phones. This trend has been primarily driven by automated equipment for laser processing of mobile phone cover glass, laser cutting devices for camera protection lenses, and intelligent equipment for laser drilling glass substrates.
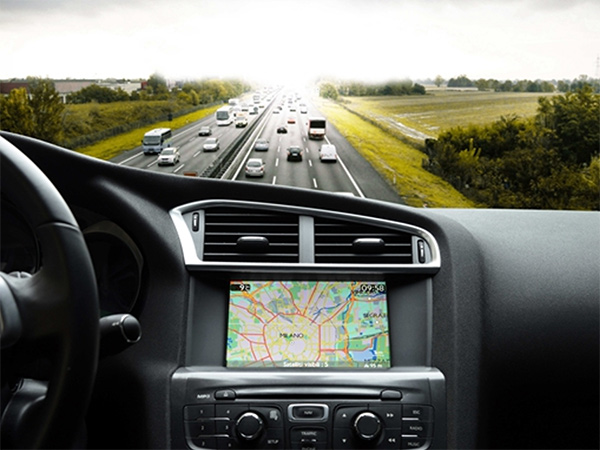
Car-Mounted Electronic Screen Glass Is Gradually Adopting Laser Cutting
Car-mounted screens consume a lot of glass panels, especially for central control screens, navigation systems, dashcams, etc. Nowadays, many new energy vehicles are equipped with intelligent systems and oversized central control screens. Intelligent systems have become standard in automobiles, with large and multiple screens, as well as 3D curved screens gradually becoming the market mainstream. Glass cover panels for car-mounted screens are widely used due to their excellent characteristics, and a high-quality curved screen glass can provide a more ultimate experience for the automotive industry. However, the high hardness and brittleness of glass pose a challenge to processing.
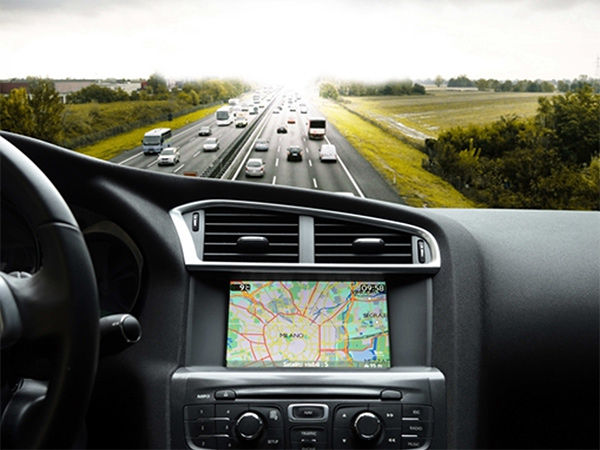

Car-mounted glass screens require high precision, and the tolerances of the assembled structural components are very small. Large dimensional errors during the cutting of square/bar screens can lead to assembly issues. Traditional processing methods involve multiple steps such as wheel cutting, manual breaking, CNC shaping, and chamfering, among others. Since it is mechanical processing, it suffers from problems such as low efficiency, poor quality, low yield rate, and high cost. After wheel cutting, CNC machining of a single car central control cover glass shape can take up to 8-10 minutes. With ultra-fast lasers of over 100W, a 17mm glass can be cut in one stroke; integrating multiple production processes increases efficiency by 80%, where 1 laser equals 20 CNC machines. This greatly improves productivity and reduces unit processing costs.
Other Applications of Lasers in Glass
Quartz glass has a unique structure, making it difficult to split cut with lasers, but femtosecond lasers can be used for etching on quartz glass. This is an application of femtosecond lasers for precision machining and etching on quartz glass. Femtosecond laser technology is a rapidly developing advanced processing technology in recent years, with extremely high processing precision and speed, capable of micrometer to nanometer-level etching and processing on various material surfaces. Laser cooling technology varies with the changing market demands. As an experienced chiller manufacturer that updates our water chiller production lines in keeping with market trends, TEYU Chiller Manufacturer's CWUP-Series Ultrafast Laser Chillers can provide efficient and stable cooling solutions for picosecond and femtosecond lasers with up to 60W.
Laser welding of glass is a new technology that has emerged in the last two to three years, initially appearing in Germany. Currently, only a few units in China, such as Huagong Laser, Xi'an Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, and Harbin Hit Weld Technology, have broken through this technology. Under the action of high-power, ultra-short pulse lasers, the pressure waves generated by lasers can create microcracks or stress concentrations in the glass, which can promote bonding between two pieces of glass. The bonded glass after welding is very firm, and it is already possible to achieve tight welding between 3mm thick glass. In the future, researchers are also focusing on the overlay welding of glass with other materials. Currently, these new processes have not yet been widely applied in batches, but once matured, they will undoubtedly play an important role in some high-end application fields.

Source: https://www.teyuchiller.com/exploring-the-current-status-and-potential-of-glass-laser-processing